Centralized Logging for WildFly with the ELK Stack
The ELK stack; elasticsearch, logstash and kibana can be used for centralize logging. It’s not the intention of this post to be a tutorial on how to configure logstash. We will go through a basic logstash configuration then configure WildFly to send log messages to logstash.
Download and Configure logstash
First we need to download logstash. Once the download is complete simply extract logstash from the archive.
Next we will need to create a configuraton file. In the logstash directory create a file called logstash-wildfly.conf and add the following content to the configuration file.
input {
tcp {
port => 8000
}
}
filter {
json {
source => "message"
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
# Use the embedded elsasticsearch for convienence
embedded => true
protocol => "http"
}
}Start logstash with the configuration file we just created ./bin/logstash agent -f logstash-wildfly.conf. In the example configuration above logstash should be listening on port 8000. Make note of the port you use as we’ll need it later when configuring WildFly.
Configure WildFly
If you don’t have a local install of WildFly you’ll want to download a recent version. In my example I’ll be use WildFly 9.0.1.Final. However any other version should work the same.
We also need to download the jboss-logmanager-ext library so that we can install it as a module. This library includes the formatter and handler we’ll use for logging.
Start up WildFly in admin-only mode so we can configure logging, $JBOSS_HOME/bin/standalone.sh --admin-only. Once the server is running start a CLI console, $JBOSS_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh -c, to install the module and configure logging. The following commands can be entered manually or placed in a CLI script.
batch
# Add the module, replace the directory on the resources attribute to the path where you downloaded the jboss-logmanager-ext library
module add --name=org.jboss.logmanager.ext --dependencies=org.jboss.logmanager,javax.json.api,javax.xml.stream.api --resources=~/tmp/jboss-logmanager-ext-1.0.0.Alpha3.jar
# Add the logstash formatter
/subsystem=logging/custom-formatter=logstash:add(class=org.jboss.logmanager.ext.formatters.LogstashFormatter,module=org.jboss.logmanager.ext)
# Add a socket-handler using the logstash formatter. Replace the hostname and port to the values needed for your logstash install
/subsystem=logging/custom-handler=logstash-handler:add(class=org.jboss.logmanager.ext.handlers.SocketHandler,module=org.jboss.logmanager.ext,named-formatter=logstash,properties={hostname=localhost, port=8000})
# Add the new handler to the root-logger
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=logstash-handler)
# Reload the server which will boot the server into normal mode as well as write messages to logstash
:reload
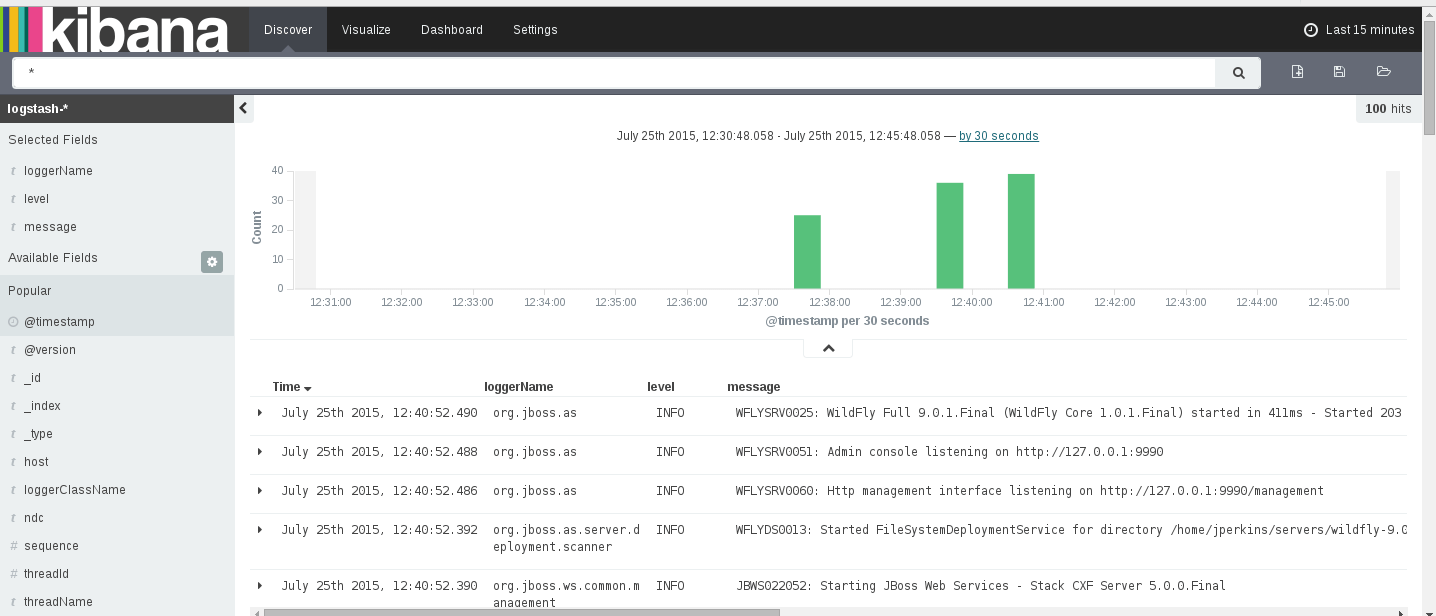
run-batchWith these changes WildFly should be writing to logstash. You can view the log messages from logstash with kibana. With the defaults we used you should just be able to start kibana with bin/kibana and the default configuration. My dashboard looks like the following.
Conclusion
If you’re already using the ELK stack for centralized logging adding WildFly to the aggregation is rather simple. If you’re just looking for a way to view and filter log messages using the ELK stack with WildFly could be a good fit as well.
One thing to note is if you’re seeing performance issues or you’re writing to a remote logstash server you may want to use an async-handler.
